- 197 Tests
- 3146 Questions
- One-off payment
What is a Watson Glaser Critical Thinking test and does it work?
Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal (W-GCTA) Briefly
Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal (W-GCTA) is a gold standard measure of critical thinking. Ever since its inception in 1925, Watson-Glaser has evolved greatly over the years. Goodwin Watson and E. M. Glaser, of Columbia Teachers College, published it as the Watson test of fair-mindedness in 1925, first administered in 1928. The measure of fair-mindedness was a success, so the test was reviewed in 1941; under Watson-Glaser Tests of Critical Thinking, and it has been revised numerous times after that, aimed to improve its efficacy. One of the most recent revision is dated in 2011, which offered a better insight on business-related trends assessment and update norm classes, and the scoring was founded on Item Response Theory. The revision also introduced an online validation test for pencil and paper test result.
Purpose of Watson Glaser Critical Thinking Test
Watson-Glaser Critical thinking test has been designed to evaluate the ability of a person to absorb information, understand its significance and assess situations based on information provided at the time. The universe is designed around the idea of diversification, in each aspect of life. Critical thinking refers to the ability of a person to consider this diverse information rationally and devise a logical view. A true critical thinker does not simply accept someone else’s conclusions and arguments but seeks his own truth. With a clear sense of self, he makes connections, judges the quality of information and analyzes the authenticity of the arguments presented.
A human mind is a complicated machine, and with the values of family and everything around a person’s life, he has to have a biased opinion and beliefs. The practice of critically evaluating one’s arguments separates opinions from facts and help him get a clear understanding of the situation.
Foundation of Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking Test
Watson-Glaser critical thinking test has been developed on the foundation of Pearson’s RED critical thinking model, which lists the skills that are needed in critical thinking and how to develop them. The RED represents:
R- Recognize Assumptions
E- Evaluate Arguments
D- Draw Conclusions
Recognize Assumptions
It is simply separating facts from opinions. To recognize assumptions mean, that a person has to view the information critically, in light of the assumptions made. This practice can be compared to separating the wheat from the chaff. The main purpose is to understand whether the information is correct or not, by uncovering the information gaps and unfounded reasons. By examining an assumption from different angles results in a richer perspective. It is advised to make sure that the fact isn’t actually an opinion in disguise.
Evaluate Arguments
In life, most of the information is tainted because people hear, what they want to hear. But to evaluate arguments is to set aside emotions, and sift through the conflicting information, objectively. People process information more accurately when they take an unbiased stand and question the underlying arguments better.
Draw Conclusions
The possession of this skill particularly refers that a person has the ability to draw conclusions based on the information underlined, supported by evidence and is classified as “good judgment”. To conclude refers to the logical result achieved by bringing together diverse information together and selecting an optimal course of action.
AREAS OF TESTING
There are five basic areas of testing for the Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking test; inferences, assumptions, deduction, interpretations, and evaluation of arguments. Every applicant has to answer questions that are logically justified for any of these areas, with the given information.
The test narrates a passage, and then a statement is given. The candidate has to pass the critical assessment of the statement that how true it is, relative to the passage narrated along with it.
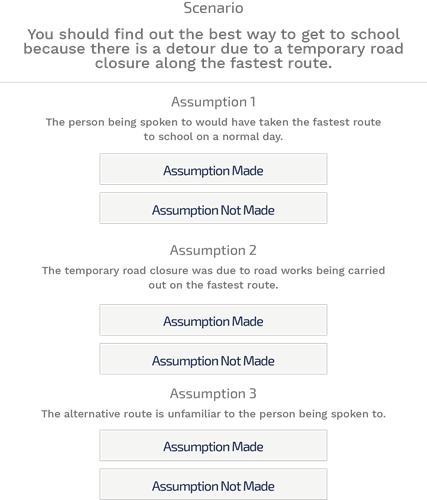
Recognizing Assumptions
The assumptions are the underlying facts that many people fail to acknowledge. In such questions, the candidates are presented with a statement. Then the statement is followed by several assumptions and the candidate has to assess whether the assumptions have been made or not.
When you say, “I will buy iPhone X next week.” You actually do not consider the underlying fact, whether you will be alive, or the payment, which is scheduled to arrive, maybe held under any pretence.
Therefore, the far granted and presupposed assumptions are marked “Yes” and if the assumption has no basis for the statement, it is marked “No”.
Inferences
Inference refers to a conclusion drawn from considered facts and observations. For example, if you hear loud voices at a distance, you may infer that someone is fighting or having a heated discussion. But the inference may or not be true. There is a possibility that the voices may belong to some a group of people, excited and just happy to live.
A candidate is given statements, which is followed by possible inferences that are to be marked as Definitely True (T), Probably True (PT), Insufficient Data (ID), Probably False (PF), and False (F).
Inferences sometimes are also based on common knowledge.
Deduction
For the test, the deduction is a conclusion given for a statement, not derived from one’s own knowledge. The test lists a passage, and then state possible statements from the passage are listed. If the statement cannot be deduced from the passage, it is marked “No” and “Yes” for the statements that can be deduced.
Interpretation
The interpretation refers to the conclusions that are drawn from a given passage, based solely on the information that is presented in the passage. For the test, it is to be assumed that all the information listed is absolutely and certainly true. The conclusions are also to be judged independently.
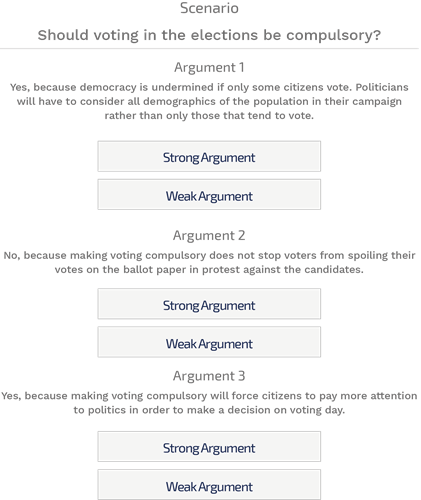
Evaluation of arguments
Evaluation of the argument refers to the selection of “Strong” and “Weak” argument status for a set of arguments, produced for a passage or a scenario. The candidates are to pass judgment based on the relevant information and sense of self.
YIELD OF WATSON-GLASER CRITICAL THINKING TEST
Watson-Glaser test has a reputation because it can be used, to predict job success ratio. Due to the proficiency of W-GCTA to do so, it is widely used, for every employer wants to know how his employee will perceive, measure, analyze and react in a situation.
The test is a preferred testing method for law firms, which in principle require higher critical thinking to support their facts versus assumptions. The Watson –Glaser critical thinking test has also been to evaluate the cognitive abilities to select future leaders, managers and hiring the right person for the right job.
DOES WATSON-GLASER CRITICAL THINKING TEST WORK?
The Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking test has a history of development spanned over 85 years, and the feedback from the clients suggest that the test is highly predictive, in terms of job success at the graduate level and above.
Watson-Glaser Predictive Validity Study 2011, shows a high correlation coefficient, which posits a strong link between barrister training success and the Watson-Glaser.
Watson-Glaser Predictive Validity Study, conducted in 2013, states that the top performers achieved the highest average score in the Watson-Glaser test, which strongly asserts that the test is highly predictive of task performance in a specific role. The study was spanned over two years, and the performance of 250 candidates was observed thoroughly.
How can Assessment-Training.com help you ace your Watson Glaser Critical Thinking Test?
Assessment-Training.com is your number 1 online practise aptitude test and assessment provider. We aim to help you ace your assessment by providing you with practise aptitude tests that mimic the tests used by employers and recruiters. Our test developers have years of experience in the field of occupational psychology and developed the most realistic and accurate practice tests available online. Our practise platform uses leading-edge technology and provides you feedback on your scores in form of test history, progress and performance to your norm group.
Check out our tailor-made Watson Glaser Critical Thinking Test Pack to fully prepare you for your assessment.
The Assessment-Training.com data science team found that through practise, candidates increased their scoring accuracy and went into their assessments more confident. Remember, you need to practice to make sure you familiarize yourself with the test formats, work on your accuracy and experience performing under time pressure.
- 10 Tests
- 126 Questions
- One-off payment
- 197 Tests
- 3146 Questions
- One-off payment
- 10 Tests
- 126 Questions
- One-off payment